Skill matrix template can be different in every organization. In the dynamic environment of today’s workforce, a “skills matrix” or sometimes referred to as a “training matrix,” plays a crucial role. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the skills matrix, exploring its significance and effective utilization in production planning and other areas. The matrix not only serves as a compass for identifying skill gaps but also acts as a strategic plan for employee development and training, ultimately enhancing productivity and efficiency in production planning.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is a Skills Matrix
A skills matrix stands as a fundamental tool within any organization, playing a vital role in managing and developing its workforce. It serves as a comprehensive visual representation that maps out and documents the diverse range of skills and competencies possessed by employees. This detailed mapping goes beyond mere record-keeping; it functions as a strategic guide, illuminating the path for individual skill development and overall workforce enhancement.
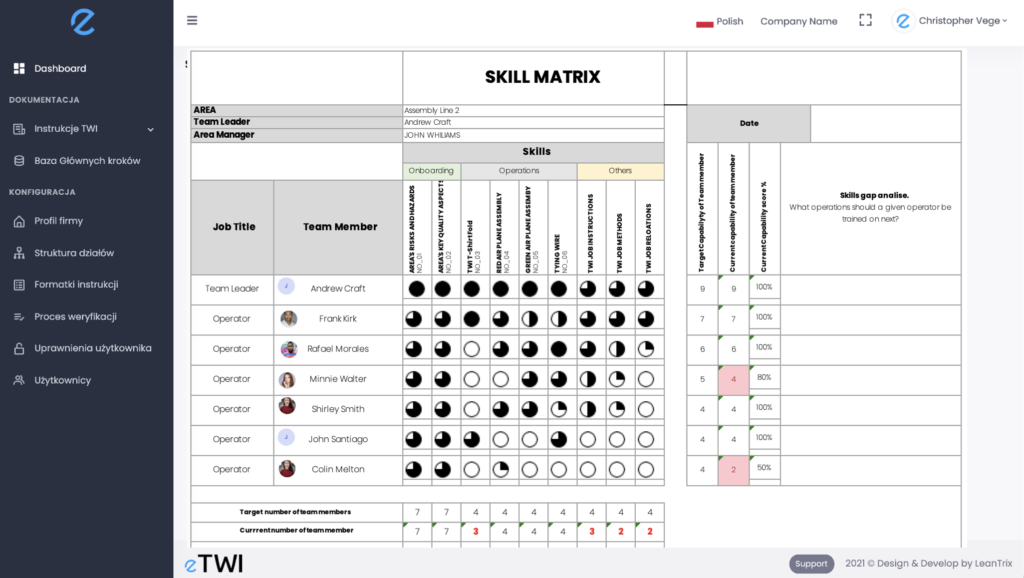
Skill Matrix Template designed by etwi software
The Significance of a Skills Matrix Template
The importance of a skills matrix in an organization cannot be overstated. It serves multiple purposes:
- Identifying Skill Gaps: By mapping the skills of employees, organizations can easily identify areas where the workforce may be lacking.
- Training and Development: It helps in planning and executing training programs, ensuring that employees are well-equipped to meet the company’s current and future needs.
- Supporting Production Planning: In the context of production, a skills matrix aids in understanding the competencies required for various tasks, thereby assisting in efficient job allocation and production planning.
Skills Matrix Template – Features
The Skill matrix template is a highly effective tool characterized by its precision in identifying training requirements across an organization. It excels in pinpointing exactly who needs training, determining the specific roles that require enhancement, establishing the optimal timing for training interventions, and identifying the most suitable trainers or training programs. This detailed approach is essential in ensuring that each training program is not just a routine procedure, but a targeted, impactful, and strategic initiative that directly contributes to the enhancement of individual and organizational performance. Skills in the Training Matrix are presented in the work instructions or SOPs. Very often SOPs can be presented in digital form via SOP Software.
A well-designed skills matrix should encompass a comprehensive range of skills and roles present within the organization. This inclusivity ensures that no area is overlooked, from technical and job-specific skills to soft skills and leadership competencies. Such a broad scope allows for a holistic view of the organization’s talent pool, facilitating more informed decision-making in talent management and succession planning.
The Quarters in a Skills Matrix
The quarters in a skills matrix reflect the employee learning curve:
- 25% Trained Operator: Represents initial, yet incomplete, training.
- 50% Operator Audited: Indicates an audit completion without meeting performance standards.
- 75% Operator Performance Achieved: Shows meeting of performance and quality standards.
- 100% Instructor: Marks the ability to train others, showing mastery.
Employees between 0-50% require supervision, while those from 75-100% work independently.
Utilization of Skills Matrix by Team Leaders
Team leaders play a pivotal role in leveraging the skills matrix as a daily management tool, essential for optimizing team performance and aligning it with the organization’s strategic objectives. The skills matrix, when used consistently, becomes a powerful instrument in their toolkit, guiding them in several key areas.
Firstly, it significantly enhances task allocation. With a comprehensive overview of their team’s skills and competencies, team leaders can assign tasks and projects more effectively, matching them with the appropriate personnel. This targeted allocation ensures efficient task completion and boosts employee satisfaction. Team members engage in work that aligns with their skills and career goals.
Secondly, the skills matrix is instrumental in identifying potential leaders within the team. It highlights individuals who possess advanced skills or who have shown rapid skill development, thereby earmarking them for leadership roles or advanced training. This proactive approach to leadership development ensures a continuous pipeline of capable leaders, vital for the organization’s future growth and stability.
Furthermore, the skills matrix plays a crucial role in future workforce planning. The skills matrix gives team leaders a clear snapshot of current skill levels. This allows them to predict future needs and skill gaps. This foresight is vital for strategic planning. Leaders can start training programs or hire new talent ahead of time. This approach prevents reacting to skill shortages at critical moments.
Linking Skills Matrix to TWI and Best Practices
The skills matrix, when integrated with Training Within Industry (TWI) programs and best practices such as those implemented by Toyota, becomes an even more powerful tool in the realm of workforce development. This combination enables organizations to follow a structured and proven approach to employee training and skill enhancement.
TWI programs have earned a reputation for effectively enhancing job training and driving continuous improvement in various industries. These programs align perfectly with the skills matrix, which acts as a blueprint to identify the specific skills and training needs of the workforce. Together, they create a cohesive system for developing a highly skilled and efficient workforce.
The role of TWI Instructor
Instructors play a crucial role in this system. They should follow a structured four-step training method. This maximizes the training programs’ effectiveness. These steps include:
- Preparation: This initial step involves understanding the needs and current skill levels of the trainees, setting clear objectives for the training, and preparing the necessary materials and resources. The skills matrix is instrumental in this phase, offering insights into the existing skill gaps and training needs.
- Presentation: In this phase, instructors present the training material to the employees. This involves not just delivering information but also demonstrating tasks and processes. The presentation should be engaging and interactive to ensure effective learning.
- Practice: After the presentation, employees should have the opportunity to practice the new skills. This hands-on experience is crucial for reinforcing the learning and ensuring that the employees can apply the skills in real-world scenarios. During this stage, instructors provide feedback and guidance to help trainees refine their skills.
- Performance Evaluation: The final step involves assessing the trainees’ newly acquired skills. This evaluation helps to determine the effectiveness of the training and whether the employees have achieved the desired skill level. The skills matrix is updated at this stage to reflect the new competencies of the workforce.
By following this structured training method, instructors can ensure systematic skill development across the organization.
Conclusion – Skill Matrix Template
In conclusion, the skills matrix is a crucial tool for every organization. It revolutionizes workforce management and development. By mapping employee skills and competencies, it clearly identifies training needs. This enhances production planning and overall organizational efficiency. Using the skills matrix strategically helps organizations identify and fill skill gaps. It ensures employees have the skills for their current roles and prepares them for future challenges.
Furthermore, the active implementation of a skills matrix fosters a culture of continuous learning and development within the organization. It encourages employees to take charge of their own skill enhancement, aligning their personal growth with the company’s strategic goals. This alignment not only boosts individual performance but also contributes to the collective success of the organization.





